Address: No. 199, Weiwu Road, Yueqing Economic Development Zone, Zhejiang Province, China.
Industrial power distribution systems require rugged plugs, high-current plugs and receptacles, and multi-receptacle configurations. These components ensure reliable power delivery when electrical equipment is constantly operating near capacity thresholds. Industries such as steel manufacturing, mineral mining, and large-scale construction require uninterrupted power delivery - a prerequisite for ensuring operational efficiency and personnel safety.

Environmental and Regulatory Assessment
Thorough environmental evaluation precedes connector selection due to significant variations in technical and regulatory requirements across applications. Petrochemical installations, characterized by volatile compounds and corrosive agents, mandate specific material corrosion resistance and ingress protection ratings. Compliance must encompass not only regional regulations but international standards such as CE marking and ROHS directives, addressing both operational safety and ecological considerations.
Evolution in certification requirements has been observed, with current standards prioritizing component traceability and mandating lead-free, recyclable materials. This progression corresponds with industrial procurement trends emphasizing sustainable infrastructure development alongside performance metrics. Technical documentation and independent verification reports are now considered essential rather than advisory.
Technical Specifications and Integration Parameters
High-current connectors are distinguished by their capacity to manage substantial loads, frequently surpassing 125 amperes. Appropriate rating determination necessitates comprehensive analysis of duty cycles, peak load conditions, and ambient temperature profiles rather than nominal value matching. Derating factors become applicable in facilities experiencing frequent equipment cycling or continuous high-load operation, rendering nominal ratings potentially inadequate.
Material selection proves critical, with engineering polymers or composite materials typically specified for demanding environments despite thermoplastic prevalence in lighter applications. These advanced materials are engineered to resist mechanical impact, ultraviolet degradation, and chemical corrosion. Contact surface integrity warrants particular examination since electrical performance stability is directly contingent upon interface durability.
Operational reliability is further enhanced through proper cable management and strain relief implementation. Accelerated conductor wear at termination points—potentially causing service interruptions or hazardous localized heating—may result from installations lacking adequate mechanical support. Risk mitigation is achieved through accessory selection including protective shrouds and positive-locking mechanisms, concurrently supporting safety protocol compliance.
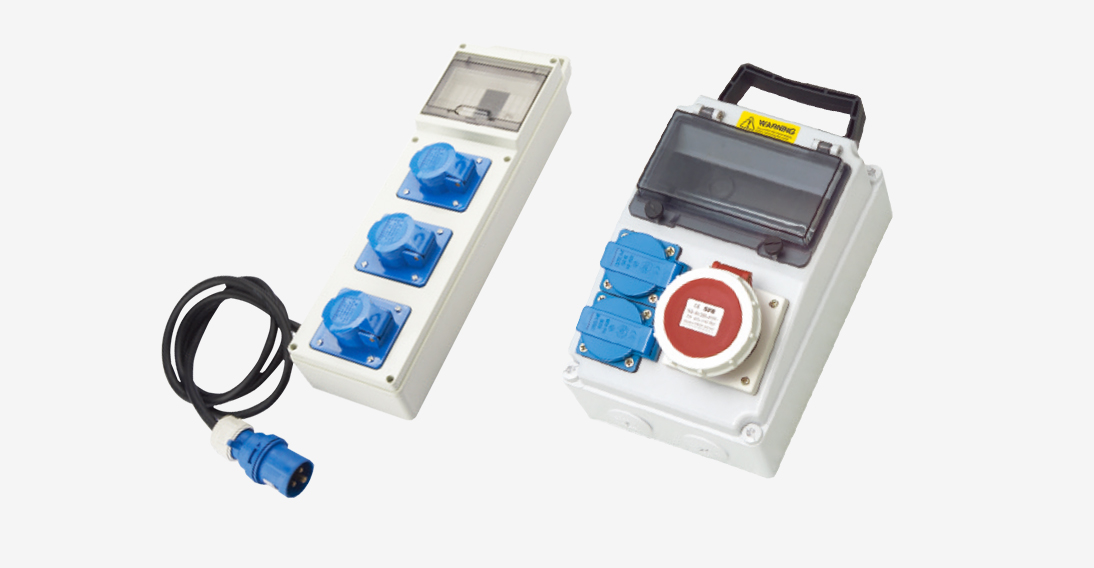
Multi-Socket System Implementation
Centralized power distribution to multiple devices is efficiently managed through purpose-built multi-socket systems, contrasting markedly with improvised extension solutions. These configurations provide discrete circuit isolation, standardized protective functions, and maintenance simplification.
Configuration evaluation requires evaluating both the total current demand and the characteristics of the individual outlets. While the combined loads can determine the baseline specification, the expected operating patterns, such as running high-demand tools simultaneously, often require additional capacity or enhanced protection. Integrated protection devices such as circuit breakers or residual current devices (RCDs) are incorporated into some designs to quickly identify and isolate faults, thereby reducing operational interruptions during electrical anomalies.
Physical layout considerations remain paramount. Spatial constraints benefit from low-profile designs that improve accessibility while reducing impact vulnerability. Conversely, high-traffic installations typically employ reinforced enclosures with clearly differentiated interfaces to prevent accidental disconnection and simplify visual identification.
Maintenance Protocols and Service Life Management
Continuous performance validation is required post-installation to maintain operational integrity and ensure adherence to evolving standards. Early degradation indicators—contact surface discoloration, housing deformation, or compromised sealing elements—are detectable through scheduled visual inspection.
Structured maintenance programs incorporate contact surface cleaning, positive-locking mechanism verification, and identification marking legibility confirmation. Integration of these procedures into routine equipment maintenance schedules represents standard practice within industrial facilities, facilitating proactive asset management.
Replacement intervals are established through correlation of manufacturer recommendations with empirical field data. Significant lifespan reduction compared to static installations may occur in applications subject to vibrational stress, thermal cycling, or frequent connection cycles.
Procurement and Documentation Requirements
Supplier engagement is optimized through partnerships with organizations demonstrating comprehensive technical documentation and transparent certification records. Detailed product specifications—encompassing cable gauge compatibility, environmental classifications, and approved installation methodologies—enable precise planning while reducing deployment-phase modification costs.
Digital resource provision by suppliers has increased substantially, with 3D models and wiring schematics now routinely available to support configuration specification. These tools are utilized to align design objectives with installation methodologies, thereby streamlining project execution.
The selection of appropriate plugs, receptacles, and accessories directly influences electrical infrastructure safety, operational efficiency, and long-term viability. Consistent performance in demanding industrial environments is achieved through meticulous planning supported by technical expertise and regulatory compliance focus.